

For example, let’s say you’re running a web server on the local PC you’re sitting in front of. It allows you to make a resource on your local PC available on the SSH server. “Remote port forwarding” is the opposite of local forwarding, and isn’t used as frequently. RELATED: What is SSH Agent Forwarding and How Do You Use It? Remote Port Forwarding: Make Local Resources Accessible on a Remote System
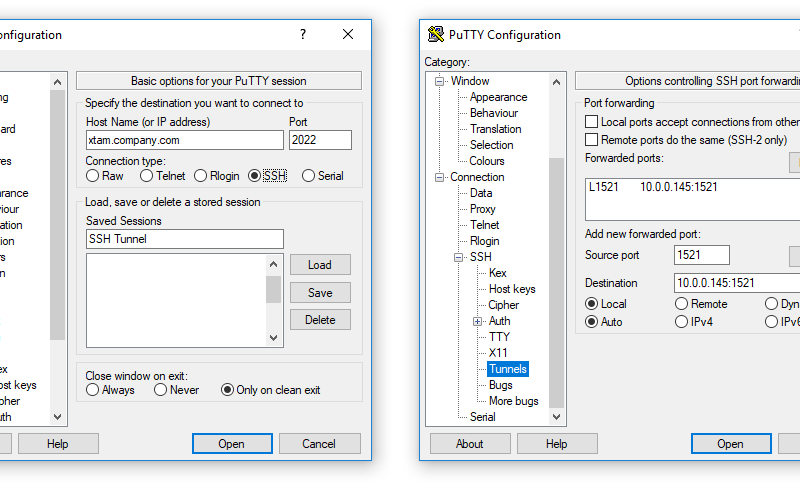
You will also need to enter the address and port of the SSH server itself on the main “Session” screen before connecting, of course. Click “Add” afterwards and then click “Open” to open the SSH connection. You can use any command line or graphical tool to access the database server as if it was running on your local PC.įor example, if you wanted to set up the same SSH tunnel as above, you’d enter 8888 as the source port and localhost:1234 as the destination. The SSH server sits in the middle, forwarding traffic back and forth. So, when you attempt to access the database server at port 1234 your current PC, “localhost”, that traffic is automatically “tunneled” over the SSH connection and sent to the database server. To do this, you establish an SSH connection with the SSH server and tell the client to forward traffic from a specific port from your local PC-for example, port 1234-to the address of the database’s server and its port on the office network. This is often the case, as it’s easier to secure a single SSH server against attacks than to secure a variety of different network resources. But if you have access to an SSH server at the office, and that SSH server allows connections from outside the office network, then you can connect to that SSH server from home and access the database server as if you were in the office. For security reasons, that database server is only configured to accept connections from the local office network. For example, let’s say you want to access a database server at your office from your home. “Local port forwarding” allows you to access local network resources that aren’t exposed to the Internet. You must ensure being uniqueness of each source port.Local Port Forwarding: Make Remote Resources Accessible on Your Local System You can also create multiple SSH tunnels.
SETUP SSH TUNNEL IN PUTTY HOW TO
How to remove an existing SSH tunnelĪny time you need to remove an existing SSH tunnel, you can simply click it in the list of forwarded ports and the ”Remove” button. Note: The source port needs to available on your local machine and the destination must be accessible from the SSH server for this to work.
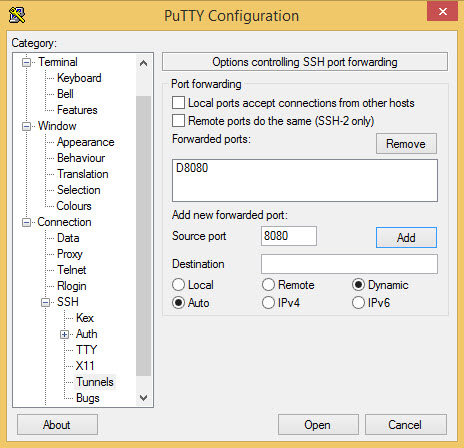
When you are connecting to the SSH server, connecting to 127.0.0.1 on port 1435 will actually connect to 10.10.1.143 port 143 via the SSH server. Next, click the ”Add” button and it will be added to the list of tunnels. Then, you must enter the destination IP address, following by a colon then the port number. That will be the port on the local machine you will connect to. You need to add a port number into the ”source port” filed to add a tunnel. As long as you leave that SSH terminal window open, all traffic to the Source Port on your local host will be forwarded on the Destination. To connect to your gateway, click ”Open” and log in.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
